If you’re tired of setting up SPAN sessions to capture network traffic transiting your network and Cisco router, it’s time to start using Cisco’s Embedded Packet Capture (EPC), available from IOS 12.4.20T and above. We will show you how to configure Cisco’s Embedded Packet Capture, to capture packets transiting a Cisco router, save them to its flash disk or export them directly to an ftp/tftp server for further analysis with the help of a packet analyzer such as Colasoft Capsa or Wireshark.
We’ve selected to Colasoft Capsa as our packet analyzer because of its amazing breakdown and presentation of captured packets.
Finally, we've also included a number of useful Embedded Packet Capture troubleshooting commands to monitor the status of the capture points and memory buffer.
Let’s take a look at some of the basic features offered by Embedded Packet Capture:
- Capture IPv4 and IPv6 packets in the Cisco Express Forwarding path
- Ability to specify various capture buffer parameters
- Export packet captures in PCAP format, enabling analysis with external tools such as Colasoft Capsa, Wireshark.
- Display content of the capture buffer
- Granularity of captured packets via Standard or ExtendedAccess Control Lists (ACLs)
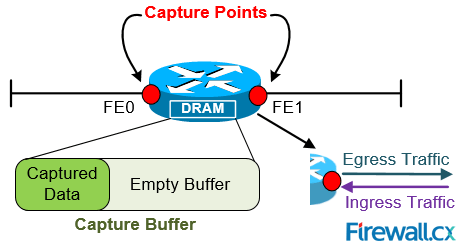 Figure 1. Understanding Basic Embedded Packet Capture Terminology
Figure 1. Understanding Basic Embedded Packet Capture Terminology
Before we dive into the configuration of Cisco EPC, let’s explain the two terms used during the EPC configuration: Capture Buffer& Capture Point. We’ll use figure 1 to help illustrate the terms.
Capture Buffer
Capture buffer is an area in memory for holding packet data. There are two types of Capture Buffers: Linear and Circular.
Linear Capture Buffer: When the capture buffer is full, it stops capturing data.
Circular Capture Buffer: When the capture buffer is full, it continues capturing data by overwriting older data.
Capture Point
Capture point is a traffic transit point where a packet is captured. Capture points need to define the following:
- IPv4 or IPv6
- CEF (Cisco Express Forwarding or Process-Switched
- Interface e.g Fast Ethernet0, Dialer0 etc.
- Direction of traffic to the interface: in (ingress), out (engress) or both
Configuring Cisco Embedded Packet Capture
EPC configuration is an easy 5 step configuration process. Examining the diagram below, our goal is to capture ingress& egress packets on interface FastEthernet0 from workstation 192.168.3.2 to and from Firewall.cx:
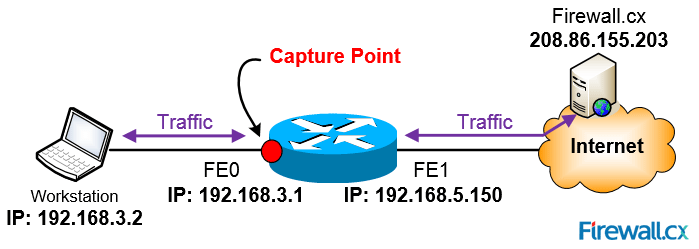 Figure 2. Capturing packets betwen host 192.168.3.2 and Firewall.cx
Figure 2. Capturing packets betwen host 192.168.3.2 and Firewall.cx
Note: None of the below configuration commands, except the optional access lists (filters), will be stored in the router's running-configuration or startup-configuration. 'Monitor' commands are only stored in the router's RAM and are lost after a router reboot.